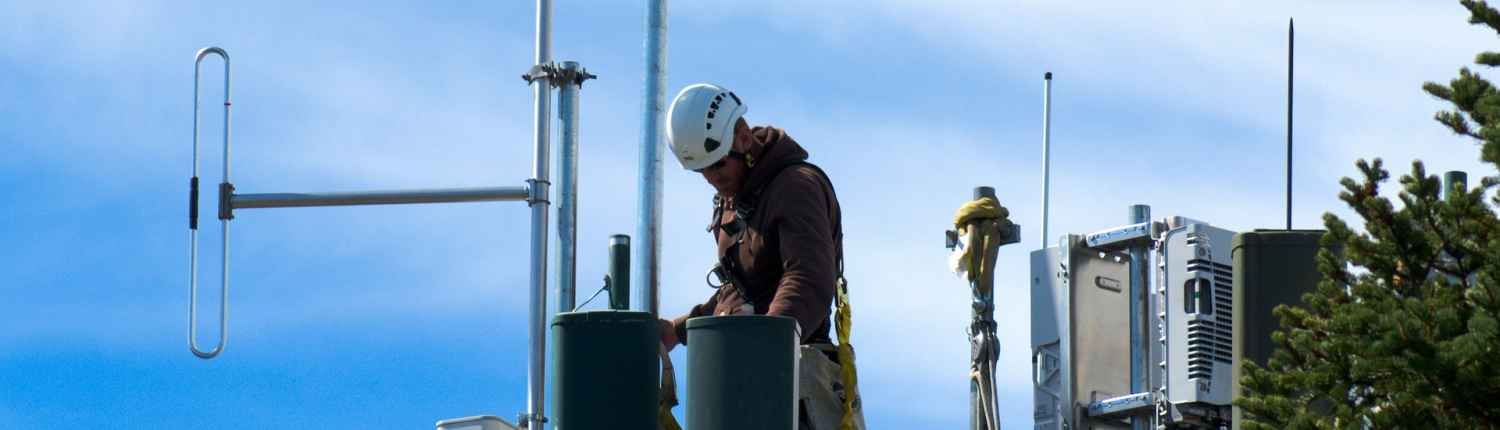
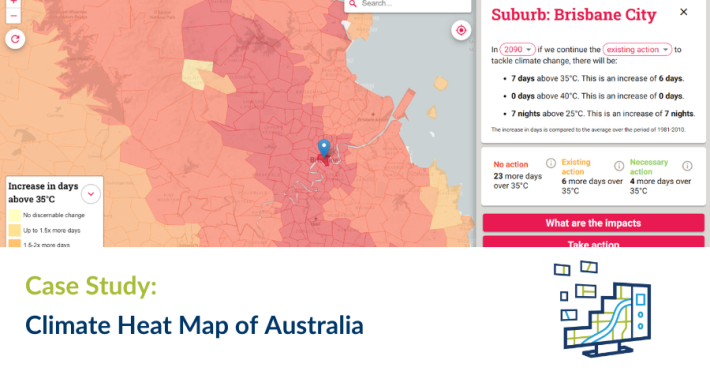
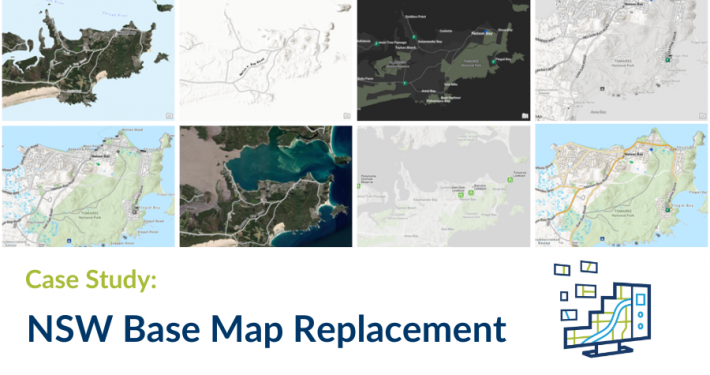
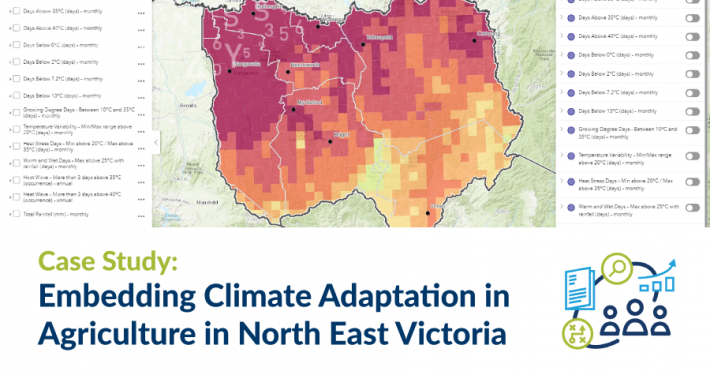
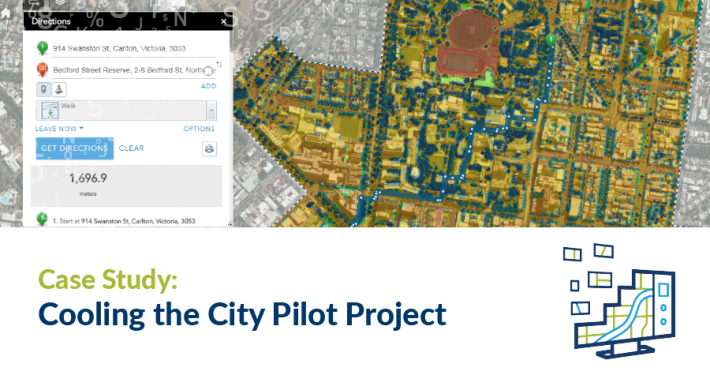
Spatial Vision has worked with Telstra to test the signal strength of a digital radio network the telecom provider constructed for a client. Utilising various spatial technologies, Spatial Vision developed a route for Telstra to drive along, continually sampling the signal strength and recording the test’s data.
This data was then sent to Spatial Vision in the form of Microsoft Access files, which contained numerous pieces of data attached to the location of each signal strength reading Telstra had performed. Primarily, Spatial Vision dealt with two pieces of data, the Bit Error Rate (BER) and the Received Signal Strength Indication (RSSI).
RSSI is, as its name implies, a measure of the signal strength that Telstra received in at any point, while the BER represents the number of errors the test received due to transmission noise.
Having divided the route into 200m x 200m grid cells, Spatial Vision then compared the BER and a RSSI value taken from the area and compared it against Telstra’s internal model for determining expected signal strength.
Telstra required Spatial Vision to randomly select the RSSI value from those taken within the area, after Spatial Vision discarded the best one.Spatial Vision then provided Telstra of the number of these 200m² cells which had met their projections, allowing Telstra to remedy areas with a high rate of bit errors or below the expected signal strength.